What is involved in an assessment for ADHD?
Summary
- You may want to know if your child has ADHD if they have difficulty paying attention, following instructions, remembering and being organised, and this is seen at home and at school.
- Some children might also have issues with hyperactive (over-active) or impulsive behaviour.
- Paediatricians and psychiatrists who work with children and adolescents can assess your child for ADHD.

It’s normal for children to have difficulty with attention, regulating their behaviour and emotions, and concentrating some of the time. These skills can also vary with a child’s age and as they develop.
If your child is having difficulty with these skills, you might notice your child:
- is easily distracted, especially when doing something they find difficult
- finds it hard to remember what they need to do
- has difficulty with social skills and making friends
- needs help to understand their emotions and manage their behaviour
- needs to move around a lot
- finds it hard to shift between tasks, especially when asked to finish something they really enjoy
- needs help with planning what they need to do, even in familiar routines like getting ready for school
- has trouble relaxing and falling asleep.
Sometimes a child’s ability to pay attention, regulate their behaviour and emotions, and concentrate will have a big impact on their day-to-day life both at home and at school.
If you are concerned that your child’s attention and behaviour are affecting their learning or the way they interact with others, it’s best to have your child’s development assessed.
How do I arrange an assessment for my child?
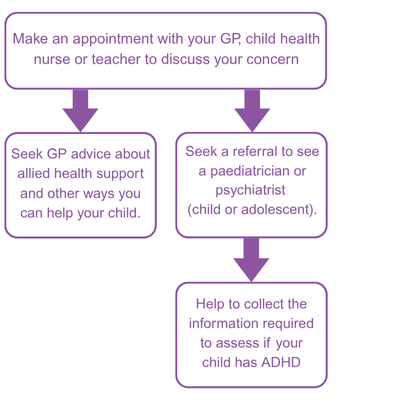
Who can assess my child for ADHD?
Paediatricians and psychiatrists who work with children and adolescents can assess your child for ADHD.Psychologists can also assess your child for ADHD but cannot prescribe medication. This means that even if a psychologist diagnoses your child with ADHD, a paediatrician will still need to assess your child and confirm the diagnosis before medication can be started.
Other professionals such as clinical nurse specialists, occupational therapists, psychologists and social workers can help you learn ways to support your child’s development at home and at school.
What is involved in an assessment for ADHD?
An interview with you and your child about:
- your child’s medical history
- their developmental history
- their psychological/social history
- your family
- any concerns you have about your child.
Completion of questionnaires by you and your child’s teacher.
An assessment of your child’s physical and mental health.
An assessment of your child’s development in other areas including:
- speech and language skills – how they communicate with others
- fine and gross motor skills – how they move their body
- social and emotional skills– how they interact with others.
They will also discuss how your child is learning and managing at school.
It is important that the assessment is thorough, as many things apart from ADHD can affect a child’s ability to pay attention and manage their behaviour.
A diagnosis of ADHD
There are guidelines that health professionals use to decide if your child has ADHD. To receive a diagnosis of ADHD your child’s presentation needs to include:- difficulties with attention and/or hyperactivity and impulsivity (not stopping to think) that are more obvious than in other children the same age
- difficulties that started before your child was 12 years old
- difficulty in their daily life at home and in another place (for example school).
To receive a diagnosis of ADHD your child’s behaviour should not be better explained by another condition (such as anxiety or autism spectrum disorder).
What happens if my child doesn’t get a diagnosis of ADHD?
You can still get help even if your child does not get a diagnosis of ADHD.
There are other health professionals that can help you and your child, such as clinical psychologists, occupational therapists and social workers.
Resources
ADHD: children & teens | Raising Children NetworkAustralian evidence-based clinical practice guideline for ADHD – Consumer Companion Guide | AADPA
Podcast Kids Health Matters (episodes 6 and 7) | Child and Adolescent Health Service
ADHD | What is ADHD & the Effects in Young People | headspace

